ARRAYS IN
JAVA (TWO-DIMENSIONAL ARRAYS)
TOPICS
· Introduction to Multidimensional
Arrays and 2-Dimensional Arrays
· Definition,
Declaration , Syntax (2-Dimensional Arrays)
· 2-Dimensional
Arrays and the .length
field
· 2-Dimensional
Array Initialization During Declaration
· 2-Dimensional Arrays and
Methods
· Common
Operations with 2-Dimensional Arrays:
·
Read
·
Print
·
Sum
·
Find max
·
Find min
·
Initialize with random
integers. Range 0 - MAX
·
Initialize with random
integers. Range MIN - MAX
Program
#1: Java Program - 2-dimensional arrays and
methods.
Program #2: Java Program
- 2-dimensional arrays and methods, processing
by row, Random.
Program #3: Java Program
- Grades problem
OUTLINE
- Some programs may require the use of an array with more
than one index (dimension) ==> need to use multidimensional arrays.
They are declared and created in basically the same way as one-dimensional
arrays. How? You simply use as many square brackets as there are indexes
(dimensions). NOTE: Each index must be enclosed in its own brackets.
- A multimdimensional array is
a collection of components, all of the same type, ordered on N dimensions
(N >= 2). Each component is accessed by N indexes, each of which
represents the component's position within that dimension.
- Just as one-dimensional arrays are tied to
count-controlled loops, multidimension-al arrays
are closely associated with nested count-controlled loops.
- Java (just like C++) has
no restrictions regarding the number of indexes ==> multidimensional
arrays may have any number of indexes, but the most common number is two.
Why? Each new index (dimension) adds a new for statement ==> too many
nested loops lead to inefficient processing.
Definition,
Declaration, Syntax:
- A two-dimensional array is a collection of a fixed
number of components arranged in rows and columns (that is, in two
dimensions), wherein all components have the same data type.
- The syntax for declaring a two-dimensional array is:
dataType[][]
arrayName = new dataType[intExp1][intExp2];
Where:
o dataType - describes the type of data stored in each
component/element of the array
o arrayName - the name of the array
o intExp1,
intExp2 -
expressions yielding positive integer values. The two expressions specify the
number of rows and the number of columns, respectively, in the array.
NOTE #1: A
2-dimensional array can be visualized as a table (matrix, grid) with the first
index giving the row, and the second index giving the column.
NOTE #2: Just
like 1-dimensional arrays, when 2-dimensional arrays are declared, every
element is automatically initialized to a "zero-equivalent" value.
Example #1: Declare a 2-dimensional array called table which will hold up to 1000 values
(of type double)
in 10 rows and 100 columns.
double[][]table
= new double[10][100];
Example #2: Declare a 2-dimensional array called matrix which will hold up to 100
values (of type int) in 20 rows and 5 columns.
int[][]matrix
= new int[20][5];
Example #3: Declare a 2-dimensional array called temps which will hold the average
temperatures for 50 U.S. states over 12 months:
double[][]temps
= new double[50][12];
- Associated with two-dimensional arrays are the concepts
of processing by row and processing by column. Such processing is
based on the idea of holding the index value constant for one dimension
while looping through the other. For example, for the array temps
declared above an average for each row will yield the anual
average temperature for each state, while an average for each column will
yield the average monthly temperature for all 50 states. Take a look at Program #2 and Program #3.
- In Java, a two-dimensional array, such as table,
is actually an array of arrays. The array a contains a reference to a
one-dimensional array of size 10 with a base type of double[]. Each indexed variable (table[0], table[1], etc.) contains a reference to a one-dimensional array
of size 100, also with a base type of double[].
- Just like in 1-dimensional arrays, in a 2-dimensional
array each element is treated exactly as a variable.
- You should reference array elements by using the index
in each dimension. To access the components of a 2-dimensional array,
you need a pair of indexes: one for the row position and one for the
column position. The syntax to access a component of a two-dimensional
array is:
arrayName[indexExp1][indexExp2]
where indexExp1 and indexExp2 are expressions yielding positive integer
values (indexExp1specifies
the row position; indexExp2
specifies the column position.) Moreover, the value of indexExp1 must be less than the number
of rows, and the value of indexExp2
must be less than the number of columns in the array.
- Examples:
- table[0][5] = 30.6;
- matrix[7][1] = 95;
- i =
table[0][5] * 92;
- System.out.println(matrix[7][1]);
- if
(table[r][c] < 14.5)...
- temps[7][1] = input.nextDouble();
- Accessing Array Elements:
public
static final int ROW = 6;
public static final int COL = 10;
...
int[][]
someArray = new int[ROW][COL];
- The first element of
array someArray --> someArray[0][0]
- Last valid index in
each dimension is one less than the size of the array in that
dimension: The last element of array someArray
--> someArray[5][9]
- Java checks for invalid
("out-of-bounds") array indexes
at compile time. If you try: someArray[6][10] = 1000; --> will cause the program to terminate with a run-time
error message.
- Array indices get out
of bounds most commonly at the first or last iteration of a loop that
processes the array: Be sure to test for this!
- A 2-dimensional array
is in bounds if: 0 <= row_index <= rowSize 1
and 0 <= column_index <= columnSize 1. If out of bounds any of them: ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException exception is thrown
- The most common
programming error made when using arrays is attempting to use nonexistent
array indexes.
Two-Dimensional
Arrays and the .length field
- Just as in one-dimensional arrays, you can use the
instance variable length to determine the number of rows as well as the
number of columns (in each row i.e. the number of elements in each row).
- .length does not give the total
number of indexed variables in a 2-dimensional array (as you have seen in programs
using 1-dimensional arrays). Because a 2-dimensional array is actually an
array of arrays, .length gives the number of rows in the array. For the same
reason, the number of columns for any row is given by .length for that row variable.
- Given a two-dimensional array matrix, the number of rows can
be determined with:
matrix.length
- Given a two-dimensional array matrix, the number of columns
can be determined with:
matrix[rowIndex].length, where rowIndex specifies the row.
- Example: The following code demonstrates how the .length variable is used:
...
for
(int r = 0; r < matrix.length;
r++)
for (int c = 0; c
< matrix[r].length; c++)
matrix[r][c] = r + c;
Two-Dimensional
Array Initialization During Declaration
- Like one-dimensional arrays, two-dimensional arrays can
be initialized when they are declared. The elements of each row are
enclosed within braces and separated by commas and all rows are enclosed
within braces.
- Example: int[][] a = { {1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}, {7, 8, 9} };
- NOTE: When storing a two-dimensional array in the computers memory, Java uses the row order form; the
first row is stored first, followed by the second row, followed by the
third row, and so on.
- Just like 1-dimensional arrays, 2-dimensional arrays
can be passed as parameters to a method and they are specified in a way
similar to 1-dimensional arrays.
- Should use the same number of sets of square brackets
as they have dimensions. In the following method, the parameter matrix
is a 2-dimensional array:
public
void someMethod(int[][]
matrix)
{ . . . }
- Methods may have a 2-dimensional array type as their
return type. The following methodreturns a
2-dimensional array of integers:
public
int[][] someMethod()
{ . . . }
Common operations
with 2-dimensional arrays:
A two-dimensional array can be processed in three ways:
- Process the entire array.
- Process a particular row of the array, called row
processing (or processing by row.)
- Process a particular column of the array, called column
processing (or processing by column.)
Because
all the components of a two-dimensional array are of the same type, the
components of any row or column are of the same type. This means that in a
two-dimensional array, each row and each column is a one-dimensional array.
Therefore, when processing a particular row or column of a two-dimensional
array, we use algorithms similar to those that process one-dimensional arrays.
The methods and the program samples below use processing for the entire array
and processing by row.
1. To read in a 2-dim array (of integers):
Import package:
import java.util.Scanner;
Class constants:
public static final int ROW = 6;
public static final int COL = 8;
Caller:
|
Solution #1: |
Solution #2: |
Method Definition:
|
Solution #1: |
|
Solution #2: |
Class constants:
public static final int ROW = 6;
public static final int COL = 8;
Caller:
|
Solution #1: |
Solution #2: |
Method Definition:
|
Solution #1: |
|
Solution #2: |
Class constants:
public static final int ROW = 6;
public static final int COL = 8;
Caller:
|
Solution #1: |
Solution #2: |
Method Definition:
|
Solution #1: |
|
Solution #2: |
Class constants:
public static final int ROW = 6;
public static final int COL = 8;
Caller:
|
Solution #1: |
Solution #2: |
Method Definition:
|
Solution #1: |
|
Solution #2: |
Class constants:
public static final int ROW = 6;
public static final int COL = 8;
Caller:
|
Solution #1: |
Solution #2: |
Method Definition:
|
Solution #1: |
|
Solution #2: |
6. To fill a 2-dim array with random integers in the range 0 - MAX:
Import package:
import java.util.Random;
Class constants:
public static final int ROW = 6;
public static final int COL = 8;
public static final int MAX = 75;
Caller:
|
Solution #1: |
Solution #2: |
Method Definition:
|
Solution #1: |
|
Solution #2: |
7. To fill a 2-dim array with random integers in the range MIN - MAX:
Import package:
import java.util.Random;
Class constants:
public static final int ROW = 6;
public static final int COL = 8;
public static final int MIN = 20;
public static final int MAX = 75;
Caller:
|
Solution #1: |
Solution #2: |
Method Definition:
|
Solution #1: |
|
Solution #2: |
8. To find sum / each row in a 2-dim array (sum by row):
Class constants:
public static final int ROW = 6;
public static final int COL = 8;
Caller:
|
Solution #1: |
Solution #2: |
Method Definition (can do much better – to be improved!):
|
Solution #1: |
|
Solution #2: |
9. To find max / each row in a 2-dim array (sum by row):
Class constants:
public static final int ROW = 6;
public static final int COL = 8;
Caller:
|
Solution #1: |
Solution #2: |
Method Definition (can do much better – to be improved!):
|
Solution #1: |
|
Solution #2: |
10. To find min / each row in a 2-dim array (sum by row):
Class constants:
public static final int ROW = 6;
public static final int COL = 8;
Caller:
|
Solution #1: |
Solution #2: |
Method Definition (can do much better – to be improved!):
|
Solution #1: |
|
Solution #2: |
Program #1: Putting together some of the most common operations for 2-dim arrays
//Two-dimensional
arrays sample program
//Arrays
and methods
import java.util.Scanner;
public class
TwoDimArray_Test1 {
public static final int ROW = 3;
public static final int COL = 4;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] a = new int[ROW][COL];
int[][] b = new int[ROW][COL];
System.out.println("Initial values/first array:
");
printArray(a, ROW, COL);
System.out.println("Initial values/second array:
");
printArray(b, ROW, COL);
System.out.print("Enter " + ROW * COL +
" integers: ");
getArray(a, ROW, COL);
System.out.println("The first array is: ");
printArray(a, ROW, COL);
//display sum
System.out.println("The sum of the elements/first
array is: " + sumArray(a, ROW, COL));
//display max
System.out.println("Max value/first array is:
" + maxArray(a, ROW, COL));
//display min
System.out.println("Min value/first array is:
" + minArray(a, ROW, COL));
//copy first array into second
copyArray(a, b, ROW, COL);
System.out.println("After copy, the second array
is: ");
printArray(b, ROW, COL);
System.out.println();
}
//Method to input data from user
public
static void getArray(int[][] matrix, int row, int col) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
for (int r = 0; r < row; r++)
for (int c = 0; c < col; c++)
matrix[r][c] = input.nextInt();
}
//Method to print the array
public static void printArray(int[][] matrix, int row, int col) {
for (int r = 0; r < row; r++){
for (int c = 0; c < col; c++)
System.out.printf("%5d", matrix[r][c]);
System.out.println();
}
}
//Method to find sum
public static int sumArray(int[][]
matrix, int row, int col) {
int sum = 0;
for (int r = 0; r < row; r++){
for (int c = 0; c < col; c++)
sum = sum + matrix[r][c];
}
return sum;
}
//Method to find max
public static int maxArray(int[][]
matrix, int row, int col) {
int max = matrix[0][0];
for (int r = 0; r < row; r++){
for (int c = 0; c < col; c++)
if(matrix[r][c] > max)
max = matrix[r][c];
}
return max;
}
//Method to find min
public static int minArray(int[][]
matrix, int row, int col) {
int min = matrix[0][0];
for (int r = 0; r < row; r++){
for (int c = 0; c < col; c++)
if(matrix[r][c] < min)
min = matrix[r][c];
}
return min;
}
//Method to copy one array into another array
public static void copyArray(int[][] source, int[][] destination, int row, int col) {
for (int r = 0; r < row; r++)
for (int c = 0; c < col; c++)
destination[r][c] = source[r][c];
}
}//close class
OUTPUT:
Initial values/first
array:
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
Initial values/second
array:
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
Enter 12 integers: 1 2
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 12 13 14
The first array is:
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9 12 13 14
The sum of the
elements/first array is: 84
Max value/first array
is: 14
Min value/first array
is: 1
After copy, the second
array is:
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9 12 13 14
Program #2: Putting together some of the most common operations for 2-dim arrays
//Two-dimensional
arrays sample program
//Arrays
and methods, row processing, Random, etc
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Random;
public class TwoDimArray_Test2 {
public static final int ROW = 5;
public static final int COL = 7;
public static final int MIN = 10;
public static final int MAX = 100;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] a = new int[ROW][COL];
int sum, largest; //
returns from methods
randArray(a, MIN, MAX);
System.out.println ("The matrix is: ");
printArray(a);
sum = sumArray(a);
largest = maxArray(a);
System.out.println ("\nThe
sum for the entire matrix is: " + sum);
sumByRow(a);
System.out.println ("\nThe
max value for the entire matrix is: " + largest);
maxByRow(a);
}
//Method to create an array using random numbers
public static void randArray(int[][] matrix, int low, int up) {
Random rand = new Random();
for (int r = 0; r < matrix.length;
r++)
for (int c = 0; c < matrix[r].length; c++)
matrix[r][c] = rand.nextInt(up - low + 1) + low;
}
//Method to print the array
public static void printArray(int[][] matrix) {
for (int r = 0; r < matrix.length;
r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < matrix[r].length; c++)
System.out.printf("%5d", matrix[r][c]);
System.out.println();
}
}
//Method to find sum for each individual row
public static void sumByRow(int[][]
matrix) {
int sum;
for (int r = 0; r < matrix.length;
r++){
sum = 0;
for (int c = 0; c < matrix[r].length; c++)
sum = sum + matrix[r][c];
System.out.println("The sum of the elements/row
" + (r + 1) + " = " + sum);
}
}
//Method to find sum/entire matrix
public static int sumArray(int[][]
matrix) {
int sum = 0;
for (int r = 0; r < matrix.length;
r++){
for (int c = 0; c < matrix[r].length; c++)
sum = sum + matrix[r][c];
}
return sum;
}
//Method to find max in each row
public static void maxByRow(int[][]
matrix){
int max;
for (int r = 0; r < matrix.length;
r++) {
max = matrix[r][0];
for (int c = 1; c < matrix[r].length; c++)
if (max < matrix[r][c])
max = matrix[r][c];
System.out.println("The largest element/row
" + (r + 1) + " = " + max);
}
}
//Method to find max/entire matrix
public static int maxArray(int[][]
matrix) {
int max = matrix[0][0];
for (int r = 0; r < matrix.length;
r++)
for (int c = 0; c < matrix[r].length; c++)
if(matrix[r][c] > max)
max = matrix[r][c];
return max;
}
}//close class
OUTPUT:
The matrix is:
59 20 45 16 76
97 74
10 27 53 47 48
14 30
90 15 62 61 41
74 95
91 87 37 68 14
50 18
65 22 33 97 25
15 69
The sum for the
entire matrix is: 1745
The sum of the elements/row 1 =
387
The sum of the
elements/row 2 = 229
The sum of the
elements/row 3 = 438
The sum of the
elements/row 4 = 365
The sum of the
elements/row 5 = 326
The max value for
the entire matrix is: 97
The largest elements/row 1 = 97
The largest
elements/row 2 = 53
The largest
elements/row 3 = 95
The largest
elements/row 4 = 91
The largest
elements/row 5 = 97
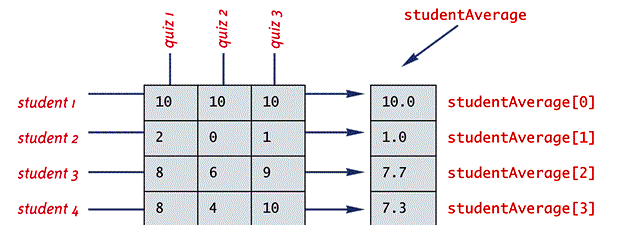
Program #3: Grades roblem - process quiz scores. Compute max and avg quiz/class. Compute max and avg quiz/each student.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TwoDimArray_Grades {
public
static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] grades = { {10, 10, 10}, {2, 0, 1}, {8, 6,
9}, {8, 4, 10}};
int largest;
double avg;
System.out.println ("The student/quiz table
is:");
printArray(grades);
avg = avgArray(grades);
largest = maxArray(grades);
System.out.println ("\nThe
max quiz / entire class is: " + largest);
maxByRow(grades);
System.out.printf("\nThe
average quiz / entire class is: %4.1f\n", avg);
avgByRow(grades);
}
//Method to print the array
public static void printArray(int[][] matrix) {
for (int r = 0; r < matrix.length;
r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < matrix[r].length; c++)
System.out.printf("%5d", matrix[r][c]);
System.out.println();
}
}
//Method to find avg for each row
public static void avgByRow(int[][]
matrix) {
int sum;
for (int r = 0; r < matrix.length;
r++){
sum = 0;
for (int c = 0; c < matrix[r].length; c++)
sum = sum + matrix[r][c];
System.out.print("Avg
quiz/student " + (r + 1) + " = ");
System.out.printf("%4.1f\n", (double)sum /
matrix[r].length);
}
}
//Method to find average/array
public static double avgArray(int[][] matrix) {
int row = matrix.length,
col = matrix[0].length;
int sum = 0;
for (int r = 0; r < row; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < col; c++)
sum = sum + matrix[r][c];
}
return (double)sum / (row * col);
}
//Method to find max for each row
public static void maxByRow(int[][]
matrix){
int max;
for (int r = 0; r < matrix.length;
r++) {
max = matrix[r][0];
for (int c = 1; c < matrix[r].length; c++)
if (max < matrix[r][c])
max = matrix[r][c];
System.out.println("Max quiz/student " + (r
+ 1) + " = " + max);
}
}
//Method to find max/array
public static int maxArray(int[][] matrix) {
int max = matrix[0][0];
for (int r = 0; r < matrix.length;
r++)
for (int c = 0; c < matrix[r].length; c++)
if(matrix[r][c] > max)
max = matrix[r][c];
return max;
}
}
OUTPUT:
The student/quiz table
is:
10 10 10
2 0 1
8 6 9
8 4 10
The max quiz /
entire class is: 10
Max quiz/student 1 =
10
Max quiz/student 2 = 2
Max quiz/student 3 = 9
Max quiz/student 4 =
10
The average quiz /
entire class is: 6.5
Avg quiz/student 1 = 10.0
Avg quiz/student 2 = 1.0
Avg quiz/student 3 = 7.7
Avg quiz/student 4 = 7.3
Additional Resources:
1. (Sun) API specification for version 6 of the Java Platform, Standard
Edition: http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/
2. (Sun) The Java Tutorials, Arrays: http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/java/nutsandbolts/arrays.html
References:
[1] Building Java Programs: A Back to Basics Approach, by Stuart Reges, and Marty Stepp, Addison
Wesley, 2008.
[2] Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, by D.S. Malik,
Thomson Course Technology, 2008